Income Tax e-Filing
What is Income tax?
Income tax is one of the most fundamental taxes any individual/business has to pay to the government on their income/profits. Income tax generated through the taxation system is directly contributed towards infrastructural development as well as towards payment of salaries of the central government employees. In this article, we will learn about income tax e-filing and all things related to the tax levied on individuals as well as businesses
In India, the income tax is classified into two types:
- Direct Taxes - Taxes Levied on your salary/profit(for businesses).
- Indirect Taxes- Taxes levied on goods and services you purchase for eg. Online Shopping, Food in restaurant, Movie tickets etc
The income tax taxation system in India is governed under the regulation specified in the Income Tax Act of 1961. This does not imply that the laws related to the income tax in India are archaic because there have been several amendments to the laws since its implementation.
Who pays the Income Tax?
In India, any individual under the age of 60 years, is eligible to pay the Income Tax (income higher than 2.5 Lakhs per annum). In addition to this, the following entities who generate income/profits are also liable to pay the income tax:
- Salaried Individuals
- Businesses
- Hindu Undivided Family(HUF)
- Body of Individuals (BOA)
- Association of Persons (AOP)
- Local Authorities
- Corporate Firms
- Companies
- Artificial Judicial Person
How is Income Tax collected?
The income tax in India is collected by the Central Government in several ways. These are enlisted below:
- TDS: The concept of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)was introduced with an aim to collect tax from the very source of income. As per this concept, a person (deductor) who is liable to make payment of specified nature to any other person (deductee) shall deduct tax at source and remit the same into the account of the Central Government
- Self-Assesment Taxes paid before filing Income Tax Returns or ITR
Read: Types of Assessments under Income Tax
- Advance Tax Payments
Where is Income tax applicable?
The income tax is applicable to profits as well as incomes of varying kinds. Here, we define which all heads/ sources of incomes are taxable under the Income Tax system. Basically, there are 5 heads of income which are taxable and they are as follows:
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="flash" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.4" animation_offset=""]
| Taxable Income Head |
Nature of the Income/Capital Gain Covered |
| Income from Salary |
Income generated by individuals from salary as well as a pension is covered in this head of income |
| Income from other sources |
Income generation from savings bank account interest, Fixed deposits, Winnings from competitions like "KBC" |
| Income from House/Property |
Income you get in the form of rent from your tenants |
| Capital Gains Income |
Income generated from the sale of a capital asset such as mutual funds like ELSS, shares, house/property |
| Income from Profession and Business |
People who are self-employed, work as a freelancer or contractor, or you run a business. Life Insurance Agents, Chartered Accountants, Doctors, Lawyers etc having their own practice |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates / Tax Rates Slabs for FY 2018-19
The income tax for people of different incomes/profits is different and it is classified under various slabs for every taxpayer. Here we list down the various Income Tax Slabs for all taxpayers.
Income Tax Rates for Individual Tax Payer & HUF (Up to 60 years Old)
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Income Tax Slabs |
Tax Rate |
Health and Educational Cess |
| Income up to ₹ 2,50,000 |
No Tax |
|
| Income Range ₹ 2,50,000- ₹5,00,000 |
5% |
4% of Income Tax |
| Income Range ₹ 5,00,000- ₹10,00,000 |
20% |
4% of Income Tax |
| Income Above ₹ 10,00,000 |
30% |
4% of Income Tax |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates for Senior Citizens (60-80 Years Old)
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Income Tax Slabs |
Tax Rate |
Health and Educational Cess |
| Income up to ₹3,00,000 |
No Tax |
|
| Income Range ₹ 3,00,000- ₹5,00,000 |
5% |
4% of Income Tax |
| Income Range ₹ 5,00,000- ₹10,00,000 |
20% |
4% of Income Tax |
| Above ₹10,00,000 |
30% |
4% of Income Tax |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates for Super Senior Citizens (80 years +)
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Income Tax Slabs |
Tax Rate |
Health and Educational Cess |
| Income up to ₹5,00,000 |
No Tax |
|
| Income up to ₹5,00,000 - ₹10,00,000 |
20% |
4% of Income Tax |
| Income ₹10,00,000 |
30% |
4% of Income Tax |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates for Cooperative Socities
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Turnover Particulars |
Tax Rate |
| Taxable income less than ₹ 10,000 |
10% |
| Taxable Income between ₹ 10,000- ₹20,000 |
20% of the amount exceeding the ₹10,000 |
| Taxable income greater than ₹ 20,000 |
30% of the amount exceeding the ₹20,000 |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates for Domestic Companies
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Turnover Particulars |
Tax Rate |
| Gross turnover upto ₹ 250 Crores |
25% |
| Gross turnover greater ₹ 250 Crores |
29% |
[/fusion_table]
Income Tax Rates for Foreign Companies
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Turnover Particulars |
Tax Rate |
| If Foreign Companies are paid by the government in form of royalties |
50% |
| Payment for Technical Services |
50% |
| Any other Services |
40% |
[/fusion_table]
Exceptions to the Tax Slabs
Not all income can be taxed on a slab basis . Capital Gains that you have are taxed on the basis of the type of asset that generates that income and how long you have been holding it. The holding time of the asset will determine wthere it is a Long Term Capital Gain (LTCG) or ashort term one. Here is a quick look into the holding period nature of asset and rate of taxes for the same in a tabular format.
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Capital Asset Type |
Holding Period |
Tax Rate |
| House Property |
Holding Less than 24 months -Short Term
Holding More than 24 months -Long Term |
20% dependent on Slab Rate |
| Debt Mutual Funds |
Holding Less than 36 months -Short Term
Holding more than 36 months -Long Term |
20% dependent on Slab Rate |
| Equity Mutual Funds |
Holding Less than 12 months -Short Term
Holding more than 12 months -Long Term |
Exempt (Till 31 March 2018 ) Capital Gains greater than 1 lakh rupees are taxable at 10% 15% |
| Shares (STT Paid) |
Holding Less than 12 months -Short Term
Holding more than 12 months -Long Term |
Exempt (Till 31 March 2018 ) Capital Gains greater than 1 lakh rupees are taxable at 10% 15% |
| Shares (STT Unpaid) |
Holding Less than 12 months -Short Term
Holding more than 12 months -Long Term |
20% As per slab rates |
| FMPs |
Holding Less than 36 months -Short Term
Holding more than 36 months -Long Term |
20% dependent on slab rates |
[/fusion_table]
How to pay Income Tax?
In India, the Income Tax can be paid via two methods:
- Online Filing of Income tax also known as Income Tax e-filing
- Offline Income Tax Filing
Online Procedure (Income Tax e-filing)
To file the income tax online you will need to visit the Tax Information Network of the Income Tax Department.
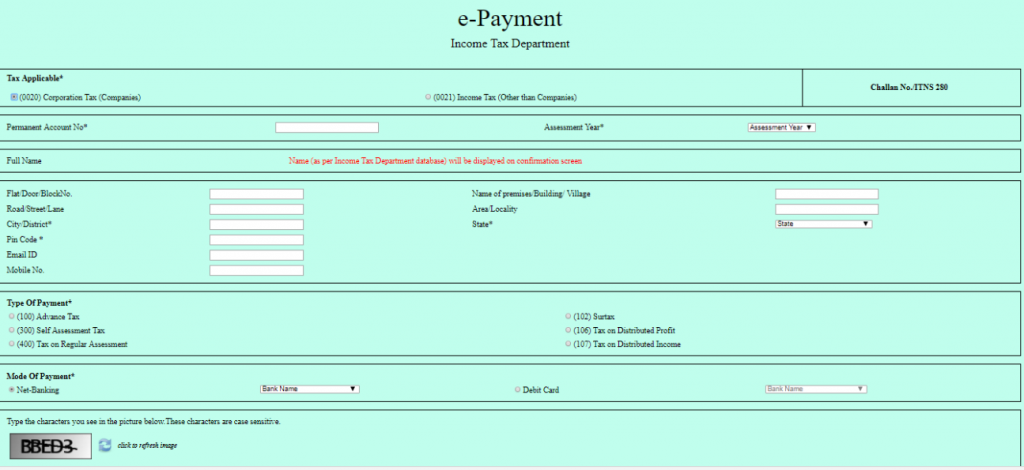
Step 1: Fill up the Challan 280
[caption id="attachment_16332" align="alignnone" width="984"]

Challan 280[/caption]
Step 2: Fill up the details with respect to the type of taxpayer you are
For eg. if you are an individual this is how you fill up the details:
- Select (0021) Income Tax (Other than companies)
- Enter PAN details
- Select Relevant Assesment Year(AY) for eg. for the financial year 1st April 2018- 31st AMrch 2019, the assessment year is 2019-20
- Enter Address
- Select Appropriate Payment Type
- Advance Tax- (100) Advance Tax
- Self Assessment Tax - (300) Self Assessment Tax
- Regular Assesment Tax - (400) Tax on Regular Assesment
- Select Payment Mode (Netbanking or Debit Card)
- Enter the given captcha correctly
- Click Proceed
[caption id="attachment_16333" align="alignnone" width="1024"]
 e-form for Income Tax e-filing[/caption]
e-form for Income Tax e-filing[/caption]
Step 3: Check and Cross-check the information provided to you as you will re-directed to the website's Payment Page
[caption id="attachment_16334" align="alignnone" width="587"]
Payment gateway: Income tax e-filing[/caption]
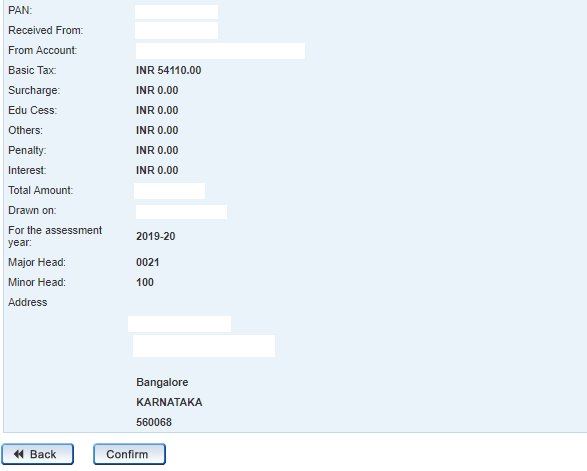
Step 4: Once you have successfully made the payment for the income tax, you will receive a tax receipt. Details of the payment along with a receipt will be given to you You will also be given a BSR Code(Basic Statistical Returns) along with the challan serial number. Keep this receipt safe with you by taking a screenshot. This receipt might be useful for future references.
[caption id="attachment_16335" align="alignnone" width="668"]
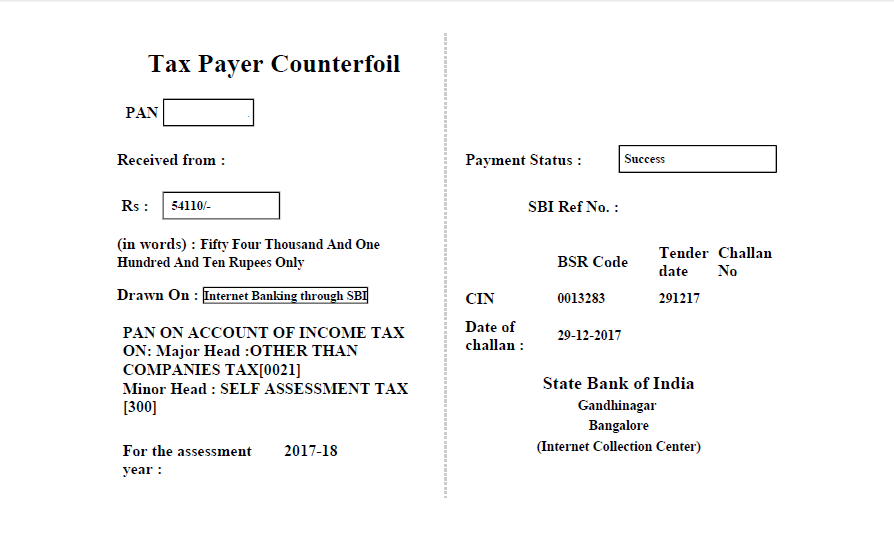
Income Tax e-filing receipt format[/caption]
In case, you forget to print a receipt of your tax payment, Login to your net banking account and retrieve it.
Offline
In the case that for some reason or the other an individual/business is unable to pay the income tax online they can avail the offline option for payment of income tax. Steps for paying income tax offline are as follows:
- Visit the nearest concerned bank and ask for tax payment challan form. The concerned form is challan 280
- Fill up the respective details of the form
- After filling up the required details submit the form and make the payment as a tax. Payment can be made either in cheque or cash. Be careful that for a large amount bank might refuse a cash payment and might ask only for a cheque. The cheque should be made in the name of "Income Tax Department "
- The official responsible for depositing the cash will provide you with a receipt against the payment of taxes. This receipt should be kept handy for future references.
Income Tax Deductions
The income tax department has introduced incentives to reduced income taxation levied on the individuals and businesses. These are the forms of income tax deductions
- Deductions under section 80 of the Income Tax Act claimed from the total income
- Deductions specific to each source of Income
Here we discuss some of the major tax deductions :
Home Ownership
- Registration as well as well as stamp duty under Section 80C
- Home Loan and Principal Interest
- First-time home-owners enjoy a benefit of ₹ 50,000 under Section 80EE of the income tax act
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Type of Deduction |
Maximum Deduction (Self-occupied House property) |
Maximum Deduction (Property on Rent) |
| Stamp Duty and Registration + Principal |
₹ 1,50,000 within the overall limit of Section 80C |
₹ 1,50,000 within the overall limit of Section 80C |
| Home Loan Interest deduction - Section 24 |
₹2,00,000 |
No Cap [Rental income should be displayed in the Income Tax return ] Maximum loss from house property has been capped at ₹ 2,00,000 |
| Deduction for first-time homeowners under Section 80 EE (Conditions Apply) |
₹ 50,000 |
- |
[/fusion_table]
Home Renting
- Many Indians move cities for work and have to rent apartments, in accordance with the same most salaried individuals get paid a House Rent Allowance or HRA for short. You should make sure that you claim tax returns if you are living in an apartment on a rental basis.
- If you are living on rent basis but don't have a provision of an HRA in your salary and in addition if you are not salaried but live on rent, you can make a claim for deduction in rent under the Section 80GG.
Medical Care/Insurance
Medical Insurance has multiple benefits for both personal coverages of healthcare expenditures as well for your family. The premiums you pay for insurance medical care schemes, as well as life insurance, are liable for tax deductions. Here are the schemes eligible for tax deductions [fusion_checklist icon="fa-briefcase-medical fas" iconcolor="" circle="" circlecolor="" size="" divider="" divider_color="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id=""][fusion_li_item icon=""] Life Insurance Premiums under Section 80C [/fusion_li_item][fusion_li_item icon=""] Medical Insurance under Section 80D [/fusion_li_item] [fusion_li_item icon=""] Preventive Checkups under Section 80D[fusion_li_item icon=""]Medical Bills [Salaried Individuals] (Standard Deduction- ₹ 40,000 effective from April 1, 2018) [/fusion_li_item][/fusion_checklist]
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Insured Person |
Deduction for Individuals upto 60 years Old |
Max Deduction 60 years and above |
| You, Spouse and , Children |
₹ 25,000 |
₹ 50,000 |
| Parents |
₹ 25,000 |
₹ 50,000 |
| Health Checkups |
₹ 5,000 |
₹ 5,000 |
| Max Deductions |
₹ 50,000 |
₹ 1,00,000 |
[/fusion_table]
Long-Term Savings/ Provident Funds
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is one of the most basic deductions that take place in an Individuals salary. Your employer will generally cut 12% of your salary package and deposit the same in a fund managed by EPFO. Individuals going for Public Provident Funds can open up a PPF account either from a post office or a public sector bank like State Bank of India (SBI) or ICICI bank. Under these, you are eligible for a few tax deductions under section 80 C of the Income Tax Act of 1961. the maximum deduction in the tax under these can go up to ₹ 1,50,000. In addition to this, contribution to NPS is a tax saving avenue for claiming a deduction under section 80CCD
Other Investment Avenues
[fusion_table fusion_table_type="1" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset=""]
| Investment |
Risk |
Interest |
Guranteed Returns |
Lock In-Period |
| ELSS Funds |
Equity-Related Risk |
12-15% (Expected) |
No |
3 years |
| NSC |
Risk-Free |
7.6% |
Yes |
5 Years |
| 5-Year Fixed Deposits |
Risk-Free |
7-9% |
Yes |
5 Years |
[/fusion_table]
Would you like assistance from an Expert?
[fusion_builder_container admin_label="" hundred_percent="no" equal_height_columns="no" menu_anchor="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="newb" id="" background_color="#e5e8ef" background_image="" background_position="center center" background_repeat="no-repeat" fade="no" background_parallax="none" enable_mobile="no" parallax_speed="0.3" video_mp4="" video_webm="" video_ogv="" video_url="" video_aspect_ratio="16:9" video_loop="yes" video_mute="yes" video_preview_image="" border_size="" border_color="" border_style="solid" margin_top="" margin_bottom="" padding_top="20px" padding_right="20px" padding_bottom="20px" padding_left="20px" admin_toggled="yes"][fusion_builder_row][fusion_builder_column type="1_1" layout="1_1" spacing="" center_content="no" hover_type="none" link="" min_height="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" background_color="" background_image="" background_position="left top" background_repeat="no-repeat" border_size="0" border_color="" border_style="solid" border_position="all" padding="" dimension_margin="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset="" last="no"][fusion_text]
Buy a CA assisted plan & Get Tax saving tips from professionals
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][fusion_builder_column type="1_4" layout="1_4" spacing="" center_content="no" hover_type="none" link="" min_height="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" background_color="" background_image="" background_position="left top" background_repeat="no-repeat" border_size="0" border_color="" border_style="solid" border_position="all" padding="" dimension_margin="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset="" last="no"][fusion_text]
Basic Package
₹399
You file your own ITR
Chat with Expert
Form 16,HRA, Rental Income
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][fusion_builder_column type="1_4" layout="1_4" spacing="" center_content="no" hover_type="none" link="" min_height="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" background_color="" background_image="" background_position="left top" background_repeat="no-repeat" border_size="0" border_color="" border_style="solid" border_position="all" padding="" dimension_margin="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset="" last="no"][fusion_text]
Savings Package
₹799
All basic plan Features
CA review of ITR
Tax saving suggestions
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][fusion_builder_column type="1_4" layout="1_4" spacing="" center_content="no" hover_type="none" link="" min_height="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" background_color="" background_image="" background_position="left top" background_repeat="no-repeat" border_size="0" border_color="" border_style="solid" border_position="all" padding="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset="" last="no"][fusion_text]
Super Package
₹1499
All savings plan features
60+ Minutes discussion with CA
Advanced advice, on Capital
Gains
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][fusion_builder_column type="1_4" layout="1_4" spacing="" center_content="no" hover_type="none" link="" min_height="" hide_on_mobile="small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility" class="" id="" background_color="" background_image="" background_position="left top" background_repeat="no-repeat" border_size="0" border_color="" border_style="solid" border_position="all" padding="" dimension_margin="" animation_type="" animation_direction="left" animation_speed="0.3" animation_offset="" last="no"][fusion_text]
Software Package
Starts at ₹99
File unlimited return for 1 year
ITR 1, 2, 3, 4, 4S and 5
Form 16 upload , store client data, direct filing
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]
 Challan 280[/caption]
Step 2: Fill up the details with respect to the type of taxpayer you are
For eg. if you are an individual this is how you fill up the details:
Challan 280[/caption]
Step 2: Fill up the details with respect to the type of taxpayer you are
For eg. if you are an individual this is how you fill up the details:
 e-form for Income Tax e-filing[/caption]
e-form for Income Tax e-filing[/caption]
 Payment gateway: Income tax e-filing[/caption]
Step 4: Once you have successfully made the payment for the income tax, you will receive a tax receipt. Details of the payment along with a receipt will be given to you You will also be given a BSR Code(Basic Statistical Returns) along with the challan serial number. Keep this receipt safe with you by taking a screenshot. This receipt might be useful for future references.
[caption id="attachment_16335" align="alignnone" width="668"]
Payment gateway: Income tax e-filing[/caption]
Step 4: Once you have successfully made the payment for the income tax, you will receive a tax receipt. Details of the payment along with a receipt will be given to you You will also be given a BSR Code(Basic Statistical Returns) along with the challan serial number. Keep this receipt safe with you by taking a screenshot. This receipt might be useful for future references.
[caption id="attachment_16335" align="alignnone" width="668"] Income Tax e-filing receipt format[/caption]
In case, you forget to print a receipt of your tax payment, Login to your net banking account and retrieve it.
Income Tax e-filing receipt format[/caption]
In case, you forget to print a receipt of your tax payment, Login to your net banking account and retrieve it.